What is EVPN?
Ethernet VPN (EVPN) is a new technology that is used to extend Ethernet circuits across Data Center and Service Provider networks. It is expected to succeed other L2VPN transport methods such as BGP-based L2VPN (RFC6624), LDP-Based L2VPN (RFC4906) and VPLS.
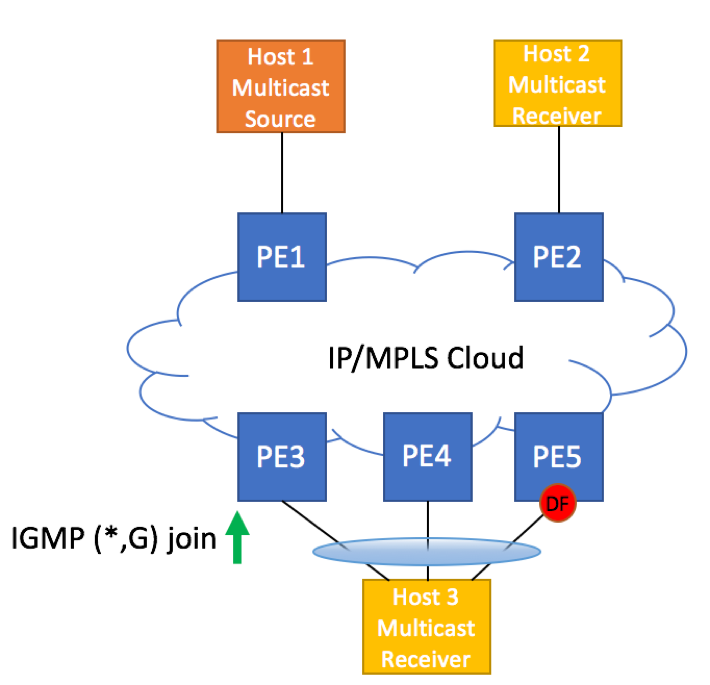
EVPN introduces a set of new features that were not available in L2VPN and VPLS environments, most noticeable of which are All-Active Multi-homing across multiple PE devices and more efficient handling of L2 Multicast traffic.
Refer to RFC 7209 to better understand the rationale for creating EVPN.
Continue reading “EVPN FAQ”